how is blood glucose levels regulated #102 control of blood glucose content
The control of blood glucose is a critical process in the human body to maintain homeostasis and ensure optimal functioning. Blood glucose refers to the concentration of sugar (glucose) present in the bloodstream. The levels of blood glucose are tightly regulated and kept within a narrow range to support various bodily functions.
Understanding Blood Sugar Regulation
 One of the main mechanisms involved in maintaining blood glucose levels is the hormonal regulation by the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ located near the stomach and plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar control.
One of the main mechanisms involved in maintaining blood glucose levels is the hormonal regulation by the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ located near the stomach and plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar control.
When the blood glucose level in the body rises, such as after consuming a meal, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin. Insulin helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, allowing them to use it as a source of energy. It also promotes the storage of excess glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use.
Conversely, when the blood glucose level drops, the pancreas secretes another hormone called glucagon. Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver and muscles and converts it back into glucose, releasing it into the bloodstream to maintain adequate glucose levels.
The Significance of Blood Sugar Homeostasis
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the normal range is essential for overall health and well-being. The body relies on glucose as a primary source of energy for all cellular activities, including brain function. Therefore, any disruptions in blood sugar regulation can have significant implications for various bodily functions.
Chronically high blood glucose levels, known as hyperglycemia, can lead to the development of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood sugar levels. It can result in a range of complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
On the other hand, excessively low blood glucose levels, known as hypoglycemia, can also be detrimental. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, fainting, and, in severe cases, even loss of consciousness. Without immediate intervention to restore blood glucose levels, it can be life-threatening.
Therefore, the finely tuned control of blood glucose through the actions of insulin and glucagon is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing the onset of various medical conditions.
Conclusion
The control of blood glucose is a complex and highly regulated process that involves the interplay of various hormones, particularly insulin and glucagon. These hormones diligently maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range, allowing the body to function optimally. Disruptions in blood sugar regulation can have severe consequences for overall health, emphasizing the importance of maintaining blood glucose homeostasis.
If you are looking for Blood Glucose Levels Chart you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Images about Blood Glucose Levels Chart like #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level, Blood Glucose Levels Chart and also Blood Glucose Levels Chart. Here it is:
Blood Glucose Levels Chart
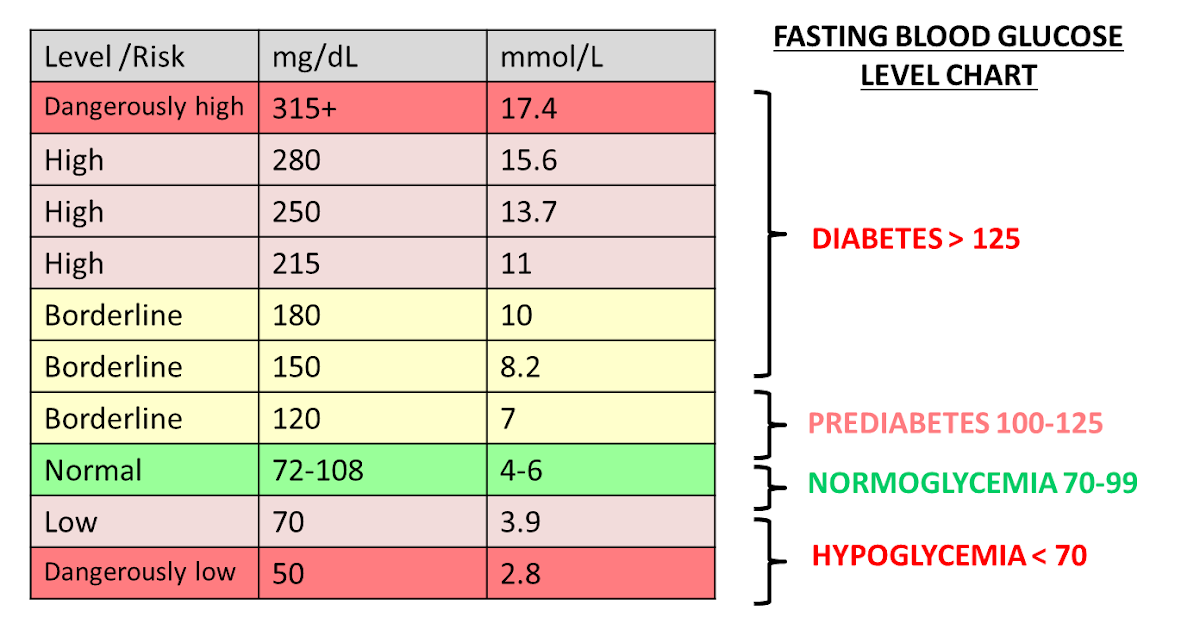 pharmwarthegame.blogspot.comblood glucose levels chart
pharmwarthegame.blogspot.comblood glucose levels chart
What Is Blood Glucose Regulation? - Nutrition Dynamics
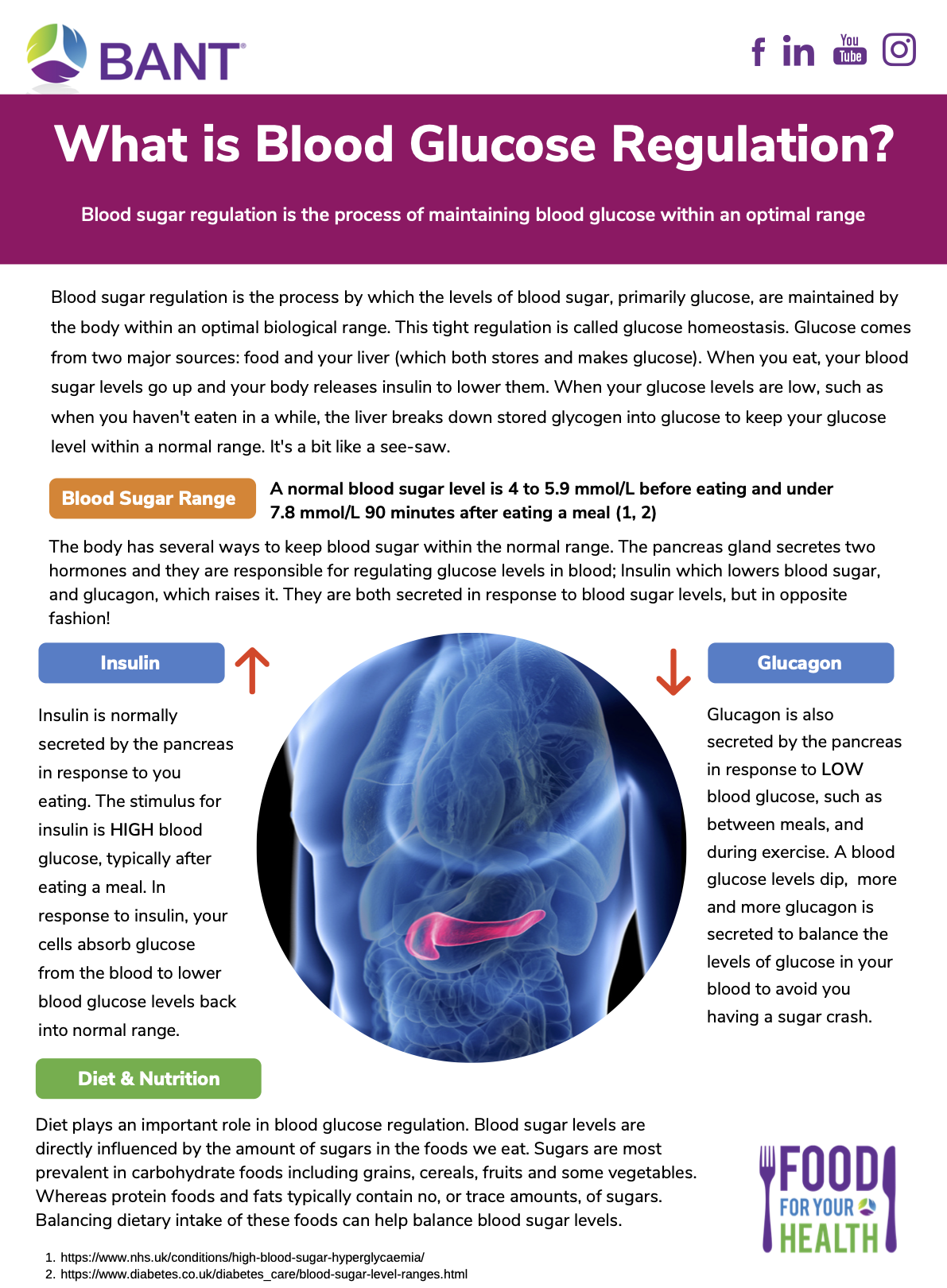 nutritiondynamics.co.ukglucose regulation
nutritiondynamics.co.ukglucose regulation
#113 The Control Of Blood Glucose | Biology Notes For A Level
 biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control level concentration summary
biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control level concentration summary
#102 Control Of Blood Glucose Content | Biology Notes For IGCSE 2014 & 2022
igbiologyy.blogspot.comglucose blood control levels normal into which bloodstream biology homeostasis igcse glycogen released drop when down gif notes broken below
Regulation Of Blood Glucose Levels
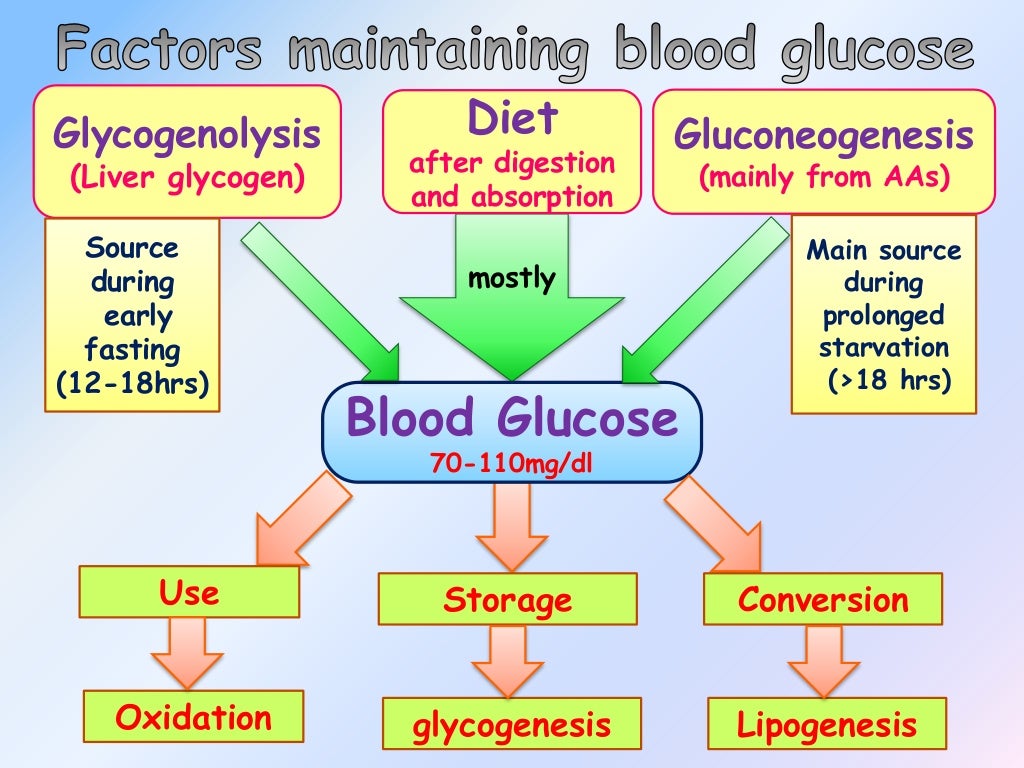 www.slideshare.netglucose regulation
www.slideshare.netglucose regulation
Blood glucose levels chart. Blood glucose control level concentration summary. What is blood glucose regulation?